New World Order Technocrats and the Surveillance State (2)
Read the first part of the article
New “Orwellian” World Order Timeline

1921, July 29 – The Council on Foreign Relations (CFR) is an American nonprofit, nonpartisan membership organization, publisher, and think tank specializing in U.S. foreign policy and international affairs. The CFR is considered to be the nation’s “most influential foreign-policy think tank”. Its membership has included senior politicians, more than a dozen Secretaries of State, CIA directors, bankers, lawyers, professors, and senior media figures. The CFR regularly convenes meetings at which government officials, global business leaders and prominent members of the intelligence/foreign-policy community discuss major international issues. The council also publishes the bi-monthly journal Foreign Affairs, and runs a think tank called the David Rockefeller Studies Program, which influences foreign policy by making recommendations to the presidential administration and diplomatic community, testifying before Congress, interacting with the media, and authoring books, reports, articles, and op-eds on foreign policy issues.
“The common interests very largely elude public opinion entirely, and can be managed only by a specialized class whose personal interests reach beyond the locality.” – Former CFR board member Walter Lippman, Public Opinion (1922).
1933, November 21 – In a letter to Col. Edward M. House, President Franklin Roosevelt writes: “The real truth of the matter is, as you and I know, that a financial element in the larger centres has owned the Government since the days of Andrew Jackson.”
1940 – British Security Coordination (BSC) was a covert organization set up in New York City by the British Secret Intelligence Service (MI6) in May 1940 upon the authorization of Prime Minister Winston Churchill. Its purpose was to investigate enemy activities, prevent sabotage against British interests in the Americas, and mobilize pro-British opinion in the Americas. As a massive propaganda campaign, the BSC influenced news coverage in the Herald Tribune, the New York Post, The Baltimore Sun, and Radio New York Worldwide.
1941, January 6 – The Four Freedoms were goals articulated by United States President Franklin D. Roosevelt on January 6, 1941. In an address known as the Four Freedoms speech (technically the 1941 State of the Union address), he proposed four fundamental freedoms that people “everywhere in the world” ought to enjoy:
• Freedom of speech;
• Freedom of worship;
• Freedom from want;
• Freedom from fear.
1941, August – The Political Warfare Executive (PWE) was a British clandestine body created to produce and disseminate both white and black propaganda, with the aim of damaging enemy morale and sustaining the morale of the occupied countries.
1941, August – The Atlantic Charter was a pivotal policy statement issued in August 1941 that, early in World War II, defined the Allied goals for the post-war world. It was drafted by the leaders of Britain and the United States, and later agreed to by all the Allies. The Charter stated the ideal goals of the war: no territorial aggrandizement; no territorial changes made against the wishes of the people; restoration of self-government to those deprived of it; free access to raw materials; reduction of trade restrictions; global cooperation to secure better economic and social conditions for all; freedom from fear and want; freedom of the seas; and abandonment of the use of force, as well as disarmament of aggressor nations. In the Declaration by United Nations of January 1, 1942, the Allies of World War II pledged adherence to this charter’s principles.
1941, December – Roosevelt devised the name “United Nations” for the Allies of World War II, and the Declaration by United Nations, on 1 January 1942, was the basis of the modern UN.
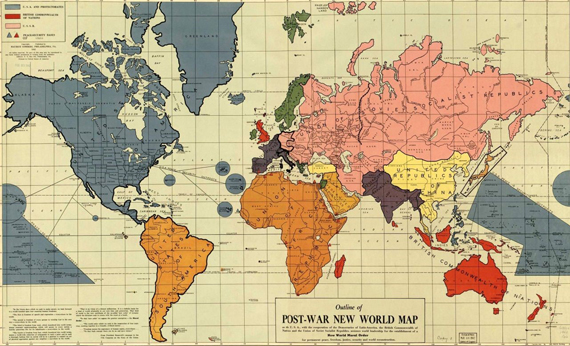
Outline of the Post-War New World Map
1942, February – The Outline of the Post-War New World Map was a map completed before the attack on Pearl Harbor and published on February 25, 1942 by Maurice Gomberg of Philadelphia. It shows a proposed political division of the world after World War II in the event of an Allied victory in which the United States of America, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union would rule. The map includes a manifesto describing a “New World Moral Order”, along with quotes from Roosevelt’s Four Freedoms speech.
1943, May 17 – BRUSA Agreement was a formal agreement to share intelligence information. It covered the exchange of personnel and joint regulations for the handling and distribution of the highly sensitive material. The security regulations, procedures and protocols for co-operation formed the basis for all SIGINT activities of both the US National Security Agency and the British GCHQ.
1945, June – The United Nations (UN) is established. At its founding, the UN had 51 member states; there are now 193. The UN Headquarters is situated in Manhattan, New York City and enjoys extraterritoriality. Further main offices are situated in Geneva, Nairobi and Vienna.
1946, March 5 – The United Kingdom – United States of America Agreement (UKUSA) is a multilateral agreement for cooperation in signals intelligence between the United Kingdom, the United States, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand.
1947, February 23 – The United World Federalists was formed by two CFR stalwarts, Norman Cousins and James P. Warburg. One of the most famous slogans of this Rockefeller front was “One world or none.”
The UWF president wanted to see established: “… once having joined the One-World Federated Government, no nation could secede or revolt … because with the Atom Bomb in its possession the Federal Government [of the World] would blow that nation off the face of the Earth.”
You will not, for example, find a UWF member today stating the group’s goals quite as crudely as a UWF professor named Milton Mayer did in 1949, when he said: “We must haul down the American flag … haul it down, stamp on it, spit on it.”
This organization was founded in Asheville, North Carolina as the result of a merger of five existing world government groups: American United for World Government; World Federalists, U.S.A.; Student Federalists; Georgia World Citizens Committee; and the Massachusetts Committee for World Federation. The United World Federalists is a non-partisan, non-profit organization with members in forty-eight states. It has 350 chapters in thirty-nine states and one chapter in Hawaii. State branches exist in twenty-seven states. The primary purpose of the organization is:
“- to achieve permanent peace through universal disarmament enforced by law;
– to release for the satisfaction of human needs the resources that at present must be used in continuous preparation for war;
– to maintain and promote human freedom, and to mobilize support for free institutions among all peoples;
– to secure to all peoples the right to develop according to their own customs and traditions.”
Membership is open to any American except persons Communist or Fascist oriented.
1948, December 10 – The concept of the Four Freedoms became part of the personal mission undertaken by First Lady Eleanor Roosevelt regarding her inspiration behind the United Nations Declaration of Human Rights, General Assembly Resolution 217A. Indeed, these Four Freedoms were explicitly incorporated into the preamble to the Universal Declaration of Human Rights which reads: “Whereas disregard and contempt for human rights have resulted in barbarous acts which have outraged the conscience of mankind, and the advent of a world in which human beings shall enjoy freedom of speech and belief and freedom from fear and want has been proclaimed the highest aspiration of the common people…”
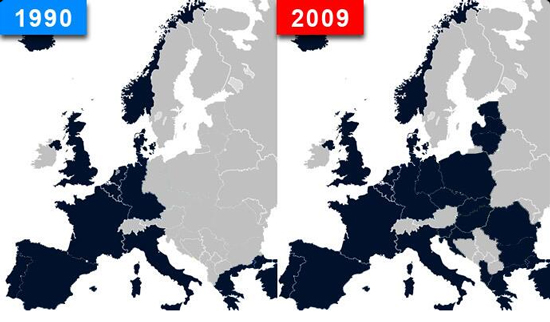
NATO expansion
1949, April 9 – The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), also called the (North) Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance based on the North Atlantic Treaty which was signed on April 4, 1949. The organization constitutes a system of collective defence whereby its member states agree to mutual defense in response to an attack by any external party. NATO’s headquarters are in Brussels, Belgium, one of the 29 member states across North America and Europe. An additional 22 countries participate in NATO’s “Partnership for Peace”, with 15 other countries involved in institutionalized dialogue programs. The combined military spending of all NATO members constitutes over 70% of the world’s defence spending.
1949, June 9 – George Orwell publishes 1984. His warnings were not heeded.
1950, February 7 – International financier and CFR member James Warburg speaking at a Senate Foreign Relations Subcommittee: “We shall have world government whether or not you like it – by conquest or consent.”
1951, April 18 – The Treaty of Paris marks the birth of the European Union.
1954, May 29 – The Bilderberg Group, Bilderberg conference, Bilderberg meetings or Bilderberg Club is an annual private conference of approximately 120 to 140 invited guests from North America and Europe, most of whom are people of influence. About one-third are from government and politics, and two-thirds from finance, industry, labour, education and communications.
1960 – The AUSCANNZUKUS alliance of intelligence operations is also known as Five Eyes. In classification markings this is abbreviated as FVEY.
Early in World War II the lack of communications interoperability between Allied Forces became a matter of concern for all nations. During March 1941 the first high-level proposals to formally structure combined operations between the United States and the United Kingdom were considered. These discussions were the genesis of the current Combined Communications Electronics Board (CCEB).
The origins of the AUSCANNZUKUS (A-Z) organization arose from dialogue between Admiral Burke, USN, and Admiral Lord Mountbatten, RN, in 1960. Their intention was to align naval communications policies and prevent, or at least limit, any barriers to interoperability with the imminent introduction of sophisticated new communications equipment. A-Z matured to the current five-nation organization in 1980 when New Zealand became a full member. This organization is firmly established and liaises closely with Washington-based management groups of the Combined Communication Electronics Board (CCEB), Multinational Interoperability Council (MIC), American, British, Canadian & Australian (ABCA (Army)), Air and Space Interoperability Council (ASIC (Air Force)), The Technical Cooperation Program (TTCP), the Quadrilateral Logistics Forum (QLF), and the International Computer Network Defense (CND) Coordination Group (ICCWG).
1961, January – Dwight D. Eisenhower warns us of the military industrial complex.
1961 – The U.S. State Department issues Document 7277, entitled Freedom From War: The U.S. Program for General and Complete Disarmament in a Peaceful World. It details a three-stage plan to disarm all nations and arm the U.N. with the final stage in which “no state would have the military power to challenge the progressively strengthened U.N. Peace Force”.
1973, July – The Trilateral Commission is a non-governmental, non-partisan discussion group founded by David Rockefeller in July 1973, to foster closer cooperation among North America, Western Europe, and Japan. To quote its founding declaration:
“Growing interdependence is a fact of life of the contemporary world. It transcends and influences national systems… While it is important to develop greater cooperation among all the countries of the world, Japan, Western Europe, and North America, in view of their great weight in the world economy and their massive relations with one another, bear a special responsibility for developing effective cooperation, both in their own interests and in those of the rest of the world.”
“To be effective in meeting common problems, Japan, Western Europe, and North America will have to consult and cooperate more closely, on the basis of equality, to develop and carry out coordinated policies on matters affecting their common interests… refrain from unilateral actions incompatible with their interdependence and from actions detrimental to other regions… [and] take advantage of existing international and regional organizations and further enhance their role.”
“The Commission hopes to play a creative role as a channel of free exchange of opinions with other countries and regions. Further progress of the developing countries and greater improvement of East-West relations will be a major concern.”

1992, May 21 – Henry Kissinger addresses to the Bilderberg organization meeting in Evian, France: “Today Americans would be outraged if U.N. troops entered Los Angeles to restore order; tomorrow they will be grateful! This is especially true if they were told there was an outside threat from beyond, whether real or promulgated, that threatened our very existence. It is then that all peoples of the world will plead with world leaders to deliver them from this evil. The one thing every man fears is the unknown. When presented with this scenario, individual rights will be willingly relinquished for the guarantee of their well being granted to them by their world government.”
1994, April 19 – Henry Kissinger addresses in the World Affairs Council Press Conference, at Regent Beverly Wilshire Hotel: “The New World Order cannot happen without U.S. participation, as we are the most significant single component.
Yes, there will be a New World Order, and it will force the United States to change its perceptions.”
2001, September 11 – Fear overcomes America, rights dissolve, liberty disappears, surveillance explodes, Orwell nods.
yogaesoteric
December 16, 2018
