„Teoria conspirației” cu nano-elemente artificiale care se auto-ansamblează în serurile Pfizer și Moderna, demonstrată într-un studiu International Journal of Vaccine Theory, Practice, and Research
Într-un amplu studiu recent despre nanotehnologia din serurile experimentale anti-covid-19, apărut în revista International Journal of Vaccine Theory, Practice, and Research, pe 18 iulie 2024, se face trimitere și către o cercetare a dr. Geanina Hagimă, publicată de ActiveNews.
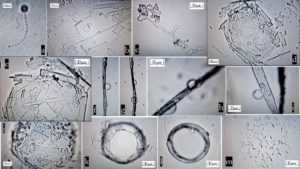
Analiza, care se bazează pe numeroase date din mai multe studii și din propriile cercetări ale autorilor, are titlul „Autoasamblarea în timp real a unor construcții artificiale vizibile prin stereomicroscop în mostre incubate din produsele ARNm, în principal de la Pfizer și Moderna: Un studiu longitudinal cuprinzător”. Poate fi descărcată în format PDF de aici. Studiul dr. Hagimă este citat astfel:
Hagimă, G. +(2023b). The Danger In The Air ‒ Rainwater Analysis Research From Romania Shows Magnetic Nanoparticles And Filaments. Comparison To Clifford Carnicom’s Rainwater Analysis, https://www.activenews.ro/opinii/EXCLUSIV-ActiveNews-CE-SE-AFLA-IN-APA-DE-PLOAIE-PERICOLUL-DIN-AER.-Dr.-Geanina-Hagima-Apel-catre-cercetatorii-romani-dar-si-catre-patriotii-din-structurile-de-aparare-si-informatii.-FOTO-prin-microscopie-electronica-si-VIDEO („Pericolul din aer: Rezultatele analizelor asupra apei de ploaie din România dezvăluie existența de nanoparticule și filamente magnetice. Comparație cu analiza apelor pluviale realizată de Clifford Carnicom”)
Pentru mai multe detalii despre analizele cercetătorului Clifford Carnicom, ale căror rezultate coincid cu cele din cercetarea dr. Geanina Hagimă, vedeți și: „Dr. Ana-Maria Mihalcea: rezultatele cercetării dr. Geanina Hagimă asupra apei pluviale coincid cu cele din analiza unui cercetător american ‒ Geoingineria, crimă împotriva umanității”.
Mai jos, oferim traducerea rezumatului studiului amplu apărut în International Journal of Vaccine Theory, Practice, and Research:
„Leziunile observate în timp real la nivel celular la primitorii serurilor anti-covid-19 «sigure și eficiente» sunt documentate [în acest studiu] pentru prima dată cu prezentarea unei descrieri și analize cuprinzătoare a fenomenelor observate. Administrarea globală a acestor produse, impuse adesea în mod obligatoriu, începând cu sfârșitul anului 2020, a dus la apariția unei multitudini de studii independente în care sunt cercetate terapiile genice injectabile cu ARN modificat, în special cele fabricate de Pfizer și Moderna. Analizele raportate aici constau în cercetări precise de laborator, având obiectivul de a înțelege de ce tot mai multe cazuri de vătămări grave debilitante, pe termen lung (și multe decese), au apărut, fără a exista niciun efect de protecție măsurabil al acestor produse comercializate agresiv.
Conținutul serurilor anti-covid-19 a fost examinat cu ajutorul unui stereomicroscop la o mărire de până la 400x. Mostre conservate cu grijă au fost cultivate în medii distincte pentru a se observa relațiile cauză-efect imediate și pe termen lung dintre seruri și celulele vii în condiții atent controlate. Din astfel de cercetări se pot desprinde concluzii rezonabile cu privire la leziunile observate la nivel mondial, care au apărut de când serurile injectabile au fost impuse forțat asupra a miliarde de oameni. Pe lângă toxicitatea celulară, descoperirile noastre dezvăluie numeroase entități artificiale ‒ de ordinul a 3~4 x 106 per mililitru de ser injectabil ‒ autoasamblante vizibile, variind de la aproximativ 1 la 100 µm sau mai mult, de diferite forme.
S-au observat entități animate asemănătoare viermilor, discuri, structuri sub formă de lanțuri, spirale, tuburi, unghiuri drepte, conținând alte entități artificiale în interiorul lor și așa mai departe. Toate acestea depășesc cu mult orice niveluri așteptate și acceptabile de contaminare a serurilor injectabile anti-covid-19, iar studiile de incubație au dezvăluit autoasamblarea progresivă a multor structuri artificiale.
În timpul incubației, pe măsură ce a trecut timpul, de-a lungul a două sau trei săptămâni, structurile simple uni- și bidimensionale au devenit mai complexe ca formă și dimensiune, dezvoltându-se în entități vizibile stereoscopic în trei dimensiuni. Acestea semănau cu filamente, funii și benzi de nanotuburi de carbon, unele apărând ca niște membrane transparente, subțiri, plate, iar altele ca spirale tridimensionale și lanțuri de mărgele. Unele dintre acestea apăreau și apoi dispăreau în timp. Observațiile noastre sugerează prezența unui tip de nanotehnologie în serurile anti-covid-19.”
Autorii:
Dr. Young Mi Lee, MD, medic practicant, Hanna Women’s Clinic Doryeong-ro 7, Republica Coreea (Coreea de Sud). Este medic specializat în obstetrică și ginecologie și endocrinolog specializat în sistemul reproducător; datorită muncii sale din ultimii trei ani, a devenit expertă în stereomicroscopie și microbiologia serurilor injectabile incubate anti-covid-19, în special de la Pfizer și Moderna.
Dr. Daniel Broudy, profesor de lingvistică aplicată la Okinawa Christian University. Deține un doctorat în psiholingvistică aplicată obținut la Școala de Comunicare și Arte Creative din cadrul Universității Deakin. Cercetările sale implică cercetări în lingvistica cognitivă, psihologia dezvoltării și psihologia socială, semiotică și teoria comunicării, în efortul de a descrie modurile în care centrele de putere organizează campanii de persuasiune și manufacturarea consimțământului pentru impunerea de politici și acțiuni la nivel transnațional. Lucrările sale au apărut în Palgrave Macmillan, Westminster University Press, Opole University Press, University Press of Wrocław, Peter Lang, Media Theory, Ethical Space: The International Journal of Ethics, Peace News, Truthout, The Asia-Pacific Journal: Japan Focus, Fast Capitalism, Propaganda in Focus și System: An International Journal of Educational Technology and Applied Linguistics.
Referințe ‒ în original:
AGC (2021). AGC Biologics’ Heidelberg Facility to Further Supply Plasmid DNA for COVID-19 Vaccine. AGC Biologics. https://www.agcbio.com/news/agc-biologics-heidelberg-facility-to-further-supply-plasmid-dna-for-covid-19-vaccine
Alamoudi, A., Celik, A., and Eltawil, A.M. (2021). Energy Efficient Capacitive Body Channel Access Schemes for Internet of Bodies, 2021 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9685810
Alavi, S.H., and Kheradvar, A. (2012). Metal mesh scaffold for tissue engineering of membranes. Tissue Eng Part C Methods, 18(4):293-301. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3311880/
Akyildiz, I. F., and Jornet, J. M. (2010). The internet of nano-things. IEEE Wireless Communications, 17(6):58-63. https://ianakyildiz.com/bwn/surveys/nanothings.pdf
Alavi, S.H., Kheradvar, A. (2012). Metal mesh scaffold for tissue engineering of membranes. Tissue Eng Part C Methods, 18(4):293-301. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3311880/
Anderson, M. (2022). The MAC Phenomenon and the intracorporeal network of nanocommunications: A review. Rumble. https://rumble.com/v15a4r1-the-mac-phenomenon-in-people-vaccinated-from-covid19.html
Bailey, M. (2022). COVID Vaccines: A Curious Discovery on the Graphene Oxide Question. Truth Comes to Light. https://drsambailey.com/resources/videos/vaccines/nz-scientist-examines-pfizer-jab-under-the-microscope/
Bailey, S. (2022). COVID Vaccines: A Curious Discovery on the Graphene Oxide Question. Dr. Sam Bailey. https://drsambailey.com/covid-vaccines-a-curious-discovery-on-the-graphene-oxide-question/
Balghusoon, A. O., and Mahfoudh, S. (2020). Routing protocols for wireless nanosensor networks and internet of nano things: a comprehensive survey. IEEE Access, 8, 200724-200748. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?arnumber=9247091
Balasubramaniam, S., and Kangasharju, J. (2013). Realizing the Internet of Nano Things: Challenges, Solutions, and Applications. Computer, 46, 62-68. https://www.computer.org/csdl/magazine/co/2013/02/mco2013020062/13rRUxNmPHo
Beattie, K. A. (2021). Worldwide Bayesian Causal Impact Analysis of Vaccine Administration on Deaths and Cases Associated with COVID-19: A BigData Analysis of 145 Countries. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/356248984_Worldwide_Bayesian_Causal_Impact_Analysis_of_Vaccine_Administration_on_Deaths_and_Cases_Associated_with_COVID-19_A_BigData_Analysis_of_145_Countries
Beattie, K.A. (2024) An Executive Summary of the Special Issue of IJVTPR — The Vaccines Were the “COVID-19 Pandemic”: An Update of Beattie’s Worldwide Bayesian Analysis of the Effects of the Experimental COVID-19 Injections on Deaths, Cases, and Excess Mortality in 210 Countries and 38 Regions. International Journal of Vaccine Theory, Practice, and Research, TBA.
Betal, S., Saha, A.K., Ortega, E., Dutta, M., Ramasubramanian, A.K., Bhalla, A.S., and Guo, R. (2018). Core-shell magnetoelectric nanorobot – A remotely controlled probe for targeted cell manipulation. Scientific Reports, 8, Article 755. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20191-w
Bigtree, D. and Cole, R. (2022 December 12). The Highwire’s Investigation of COVID Vaccines. The Highwire. https://thehighwire.com/ark-videos/the-highwires-lab-investigation-of-covid-vaccines/
Blaylock, R. L. (2021). Excitotoxicity (Immunoexcitotoxicity) as a Critical Component of the Cytokine Storm Reaction in Pulmonary Viral Infections, Including SARS-Cov-2. International Journal of Vaccine Theory, Practice, and Research, 1(2), 223–242. https://doi.org/10.56098/ijvtpr.v1i2.14
Blaylock, R. L. (2022a). Responses to comments on my paper: “COVID Update: What is the truth?” Surgical Neurology International, 13, 316. https://doi.org/10.25259/SNI_578_2022
Blaylock, R. L. (2022b). The COVID-19 “vaccines”: What is the truth? International Journal of Vaccine Theory, Practice, and Research, 2(2), 595–602. https://doi.org/10.56098/ijvtpr.v2i2.57
Burke, P., and Rutherglen, C. (2010). Toward a single-chip, implantable RFID system: Is a single-cell radio possible? Biomedical Microdevices, 12(4), 589-596. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-008-9266-4
Burkhardt, A. (2022) Notes and recommendations for conducting post-mortem examination (autopsy) of persons deceased in connection with COVID vaccination. doctors 4 covidethics.org https://doctors4covidethics.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/autopsy-directions-revised.pdf
Campra, P. (2021a). Detection of graphene in COVID-19 vaccines. Counteranalysis of COVID Vaccines. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/355979001_DETECTION_OF_GRAPHENE_IN_COVID19_VACCINES
Campra, P. (2021b). Microstructures in COVID vaccines: Inorganic crystals or Wireless Nanosensors Network? Counteranalysis of COVID Vaccines. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/356507702_MICROSTRUCTURES_IN_COVID_VACCINES_inorganic_crystals_or_Wireless_Nanosensors_Network
Cao, S., Shao, J., Xia, Y., Che, H., Zhong, Z., Meng, F., van Hest, J.C.M., Abdelmohsen, L.K.E.A., Williams, D.S. (2019). Molecular Programming of Biodegradable Nanoworms via Ionically Induced Morphology Switch toward Asymmetric Therapeutic Carriers. Small. 15(38). https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/smll.201901849
Celik, A., Khaled N. Salama, K.N., and Ahmed M. Eltawil, A.M. (2022). The Internet of Bodies: A Systematic Survey on Propagation Characterization and Channel Modelling. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 9(1):321-345. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?arnumber=9490369
Classen, J. B. (2021) COVID-19 RNA based vaccines and the risk of prion disease. Microbiology & Infectious Diseases, 5, 1–3. https://principia-scientific.com/covid-19-rna-based-vaccines-and-the-risk-of-prion-disease/
Classen, J. B. (2023). Possible Treatments for COVID Vaccine induced prion disease. Recent Advances in Clinical Trials, 3(2). https://doi.org/10.33425/2771-9057.1024
Cruz Alvarado, M. A., & Bazán, P. (2019). Understanding the Internet of Nano Things: overview, trends, and challenges. E-Ciencias de la Información, 9(1), 152-182. https://www.redalyc.org/journal/4768/476862662008/476862662008.pdf
Dambri, O. A., Cherkaoui, S., and Makrakis, D. (2022). Design and evaluation of a receiver for wired nano-communication networks. IEEE Transactions on NanoBioscience. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2009.11805.pdf
Dasdag, S., Akdag, M.Z., Erdal, M.E., Erdal, N., Ay, O.I., Ay, M.E., Yilmaz, S.G., Tasdelen, B., Yegin, K. (2015). Effects of 2.4 GHz radiofrequency radiation emitted from Wi-Fi equipment on microRNA expression in brain tissue. Int J Radiat Biol, 91(7):555-61. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25775055/
Dhuli, M.C. Medori, C., Micheletti, K., Donato, F., Fioretti, A., Calzoni, A., Praderio, M.G., De Angeli, G., Arabia, S., Cristoni, S., Nodari, M. (2023). Presence of viral spike protein and vaccinal spike protein in the blood serum of patients with long-COVID syndrome. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, 27:13-19. https://www.europeanreview.org/wp/wp-content/uploads/013-019-2.pdf
Diblasi, L. and Sangorrin, (2024). Analysis of COVID-19 Injections — 50 Undeclared Chemical Elements, Graphene Oxide, Fluorescent Particles – Conversation with Biotechnologist Lorean Diblasi. Interview with Ana Maria Mihalcea. https://anamihalceamdphd.substack.com/p/analysis-of-covid-19-injections-50
Dubuc, B., Quiniou, J.F., Roques-Carmes, C., Tricot, C., and Zucker, S. W. (1989). Evaluating the fractal dimension of profiles. Phys. Rev. A 39, 39(3):1500. https://journals.aps.org/pra/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevA.39.1500
El-Husseiny, H.M., Mady, E.A., Hamabe, L., Abugomaa, A., Shimada, K., Yoshida, T., Tanaka, T., Yokoi, A., Elbadawy, M., Tanaka, R. (2022) Smart/stimuli-responsive hydrogels: Cutting-edge platforms for tissue engineering and other biomedical applications. Materials Today Bio. https://www.x-mol.net/paper/article/1469390524673204224
Endo, Y. (2021). Development of a cell-free protein synthesis system for practical use, Proceedings of the Japan Academy, Series B, 2021, Volume 97, Issue 5, Pages 261-276 https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/pjab/97/5/97_PJA9705B-03/_html/-char/en
FDA. 2021. BLA Approval Letter. Food and Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/media/151710/download
Finn, T.M. (2011). U.S. FDA requirements for Human Vaccine Product Safety and Potency Testing Procedia in Vaccinology. 5:137-140. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1877282X11000282
Gat, I., Kedem, A., Dviri, M., Umanski, A., Levi, M., Hourvitz, A., Baum, M. (2022). COVID-19 vaccination BNT162b2 temporarily impairs semen concentration and total motile count among semen donors. Andrology, Sep;10(6):1016-1022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9350322/
Hagimă, G. (2023a). Interview. Electron Microscopy of Comirnaty, Moderna C19 Shots, Dental Anaesthetics & Pneumovax. https://rumble.com/v3xti7w-electron-microscopy-of-comirnaty-moderna-c19-shots-dental-anestetics-and-pn.html
Hagimă, G. +(2023b). The Danger In The Air – Rainwater Analysis Research From Romania Shows Magnetic Nanoparticles And Filaments. Comparison To Clifford Carnicom’s Rainwater Analysis. https://www.activenews.ro/opinii/EXCLUSIV-ActiveNews-CE-SE-AFLA-IN-APA-DE-PLOAIE-PERICOLUL-DIN-AER.-Dr.-Geanina-Hagima-Apel-catre-cercetatorii-romani-dar-si-catre-patriotii-din-structurile-de-aparare-si-informatii.-FOTO-prin-microscopie-electronica-si-VIDEO-183736
Hughes, D. A. (2022). What is in the so-called COVID-19 “vaccines”? Part 1: evidence of a global crime against humanity. International Journal of Vaccine Theory, Practice, and Research, 2(2), 455–586. https://doi.org/10.56098/ijvtpr.v2i2.52
Idrees, D. and Kumar, V. (2021) SARS-CoV-2 spike protein interactions with amyloidogenic proteins: Potential clues to neurodegeneration. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 554, 94–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.03.100
Idrees, D., Kumar, V., (2021). SARS-CoV-2 spike protein interactions with amyloidogenic proteins: Potential clues to neurodegeneration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021 May 21;554:94-98. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.03.100
Ilori, A.O., Gbadamosi, O.A., Ibitola, G.A., Ajanaku, O. (2019). Risk Assessments of Magnetic Field Radiation from AC and Battery Powered Laptop Computers. American Journal of Science and Technology. 6(2):14-19. http://www.aascit.org/journal/archive2?journalId=902&paperId=7628
Jing, Y., Peng, H., and Liu, Z. (2023). WBNN: a weight-based next neighbor selection algorithm for wireless body area network. Soft Computing. 28:1803-1818. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00500-023-09511-z
Johnson, L., Broudy, D. and Hughes, D.A. (2024a) Bringing Transhumanism Down to Earth, Part 1: Military Intelligence Operations Cloaked in the False Promise of Transcendence. Propaganda in Focus. https://propagandainfocus.com/bringing-transhumanism-down-to-earth-part-1-military-intelligence-operations-cloaked-in-the-false-promise-of-transcendence/
Johnson, L., Broudy, D. and Hughes, D.A. (2024b) Transhumanist Futures, Part 2: Humanity in the Crosshairs. Propaganda in Focus. https://propagandainfocus.com/transhumanist-futures-part-2-humanity-in-the-crosshairs/
Johnson, L., Broudy, D. and Hughes, D.A. (2024c) Military Operations in Civilian Disguise, Part 3: Bio-Nano Governance and Terms of Use for Humans 2.0. Propaganda in Focus. https://propagandainfocus.com/military-operations-in-civilian-disguise-part-3-bio-nano-governance-and-terms-of-use-for-humans-2-0/
Johnson, L., Broudy, D. and Hughes, D.A. (2024da) WHO’s Pulling the Strings? COVID Injections and the Internet of Bio-Nano Things, Part 4: Testing New Human Nodes of Connectivity. Propaganda in Focus. https://propagandainfocus.com/whos-pulling-the-strings-covid-injections-and-the-internet-of-bio-nano-things-part-4-testing-new-human-nodes-of-connectivity/
Jornet, J.M and Akyildiz, I.F. (2014). Graphene-based Plasmonic Nano-Antenna for Terahertz Band Communication in Nanonetworks, IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 31(12):685-694. https://web.archive.org/web/20170810210901id_/http://bwn.ece.gatech.edu/papers/2014/c1.pdf
Kashani, Z.A., Pakzad, R., Fakari, F.R., Haghparast, M.S., Abdi, F., Kiani, Z., Talebi, A., Haghgoo, S.M. (2023). Electromagnetic fields exposure on fetal and childhood abnormalities: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Open Med (Wars), 12;18(1):20230697. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10183723/
King Abdullah University. (2021). A network of body monitoring devices using our own tissue as the basis for the internet of bodies. Physics.Org. https://phys.org/news/2021-11-network-body-devices-tissue-basis.html
Kingston, K. 2023. (2023). mRNA is an Operating System – Technology Platform per Moderna Website. The Kingston Report. https://karenkingston.substack.com/p/mrna-is-an-operating-system-technology
Khan, T., Civas, M., Cetinkaya, O., Abbasi, N. A., and Akan, O. B. (2020). Nanosensor networks for smart health care. In Nanosensors for Smart Cities (pp. 387-403). Elsevier. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Oktay-Cetinkaya-2/publication/339260608_Nanosensor_networks_for_smart_health_care/links/600c738292851c13fe3206c6/Nanosensor-networks-for-smart-health-care.pdf
Kyrie, V. and Broudy, D. (2022). Cyborgs R Us: The bio-nano panopticon of injected bodies? International Journal of Vaccine Theory, Practice, and Research, 2(2), 355-383. https://doi.org/10.56098/ijvtpr.v2i2.49
Lee, S.J., Jung, C. A., Choi, K., and Kim, S. (2015). Design of wireless nanosensor networks for intrabody application. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 11(7), Art. no. 176761. http://csc.columbusstate.edu/lee/publications/IJDSN_176761-2015.pdf
Leung, W.-Y., Wu, H.H.L., Floyd, L., Ponnusamy, A., Chinnadurai, R., (2023). COVID-19 Infection and Vaccination and Its Relation to Amyloidosis: What Do We Know Currently? Vaccines, 11(7):1139. https://www.mdpi.com/2076-393X/11/7/1139
Li, L., Yu, Z., Liu, J., Liu, J., Yang, M., Shi, G., Feng, Z., Luo, W., Ma, H., Guan, J., Mou, F. (2023). Swarming Responsive Photonic Nanorobots for Motile-Targeting Microenvironmental Mapping and Mapping-Guided Photothermal Treatment. Nano-Micro Lett. 15,141 https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-023-01095-5
Lyons-Weiler, J. (2020). Pathogenic priming likely contributes to serious and critical illness and mortality in COVID-19 via autoimmunity. Journal of Translational Autoimmunity, 3, 100051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtauto.2020.100051
Maervoet, V.E.T. and Briers, Y. (2017) Synthetic biology of modular proteins. Bioengineered, Taylor & Francis. 8, 196–202. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2016.1222993
Marik, P. (2023). Bombshell Study on Vaccine ‘Ribosomal Frameshifting’. Epoch News. https://www.theepochtimes.com/epochtv/bombshell-study-on-vaccine-ribosomal-frameshifting-dr-paul-marik-atlnow-5548921?&utm_medium=AmericanThoughtLeaders&utm_source=SocialM&utm_campaign=PaulMarik&utm_content=12-18-2023
Marsudi, M.A., Ariski, R.T., Wibowo, A., Cooper, G., Barlian, A., Rachmantyo, R., Bartolo, P.J.D.S. (2021). Conductive Polymeric-Based Electroactive Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering Applications: Current Progress and Challenges from Biomaterials and Manufacturing Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22(21):11543. https://doi.org/10.3390/ ijms222111543
Martin, A. (2024). The Messenger. Connecticut College. http://www.conncoll.edu/news/cc-magazine/past-issues/2021-issues/winter-2021/the-messenger/
Martins, N. R., Angelica, A., Chakravarthy, K., Svidinenko, Y., Boehm, F. J., Opris, I., Lebedev, M. A., Swan, M., Garan, S. A., Rosenfeld, J. V., Hogg, T., and Freitas, R. A. (2019). Human brain/cloud interface. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 13, Article 112. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.00112
McKernan, K., Helbert, Y., Kane, L. T., & McLaughlin, S. (2023). Sequencing of bivalent Moderna and Pfizer mRNA vaccines reveals nanogram to microgram quantities of expression vector dsDNA per dose. OSF. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/b9t7m
Mead, M.N., Seneff, S., Wolfinger, R., Rose, J., Denhaerynck, K., Kirsch, S. et al. (2024a). COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines: Lessons Learned from the Registrational Trials and Global Vaccination Campaign. Cureus, Cureus. 16. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.52876
Mead, M. N., Seneff, S., Wolfinger, R., Rose, J., Denhaerynck, K., Kirsch, S., & McCullough, P. A. (2024b). COVID-19 modified mRNA „vaccines”, Part 1: Lessons learned from clinical trials, mass vaccination, and the bio-pharmaceutical complex. International Journal of Vaccine Theory, Practice, and Research, 3(1), 1112–1178. https://doi.org/10.56098/fdrasy50
Mead, M. N., Seneff, S., Wolfinger, R., Rose, J., Denhaerynck, K., Kirsch, S., & McCullough, P. A. (2024c). COVID-19 modified mRNA “vaccines”, Part 2: Lessons learned from clinical trials, mass vaccination, and the bio-pharmaceutical complex. International Journal of Vaccine Theory, Practice, and Research, 3(1)
Moderna. (2022). Moderna Announces First Participants Dosed in Phase 2/3 Study of COVID-19 Vaccine Candidate in Pediatric Population. https://wikispooks.com/wiki/Moderna_COVID-19_vaccine#cite_note-9
Moon, J.H. (2020). Health effects of electromagnetic fields on children. Clin Exp Pediatr, 63(11):422-428. https://www.e-cep.org/journal/view.php?doi=10.3345/cep.2019.01494
Mousavi, S.M., Hashemi, S.A., Gholami, A., Mazraedoost, S., Chiang, W-H., Arjmand, O., Omidifar, N., Babapoor, A. (2021). Precise Blood Glucose Sensing by Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots for Tight Control of Diabetes, Journal of Sensors, vol. 2021 https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5580203
Mulroney, T.E., Pöyry, T., Yam-Puc, J.C., Rust, M., Harvey, R.F., Kalmar, L. et al. (2023) N1-methylpseudouridylation of mRNA causes +1 ribosomal frameshifting. Nature, 625, 189–94. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06800-3
Murakami, H. (2023). Professor Murakami discusses cancer promoting DNA sequence in Pfizer jab. Rumble. https://rumble.com/v2m9732-malicious-prof.-murakami-discusses-cancer-promoting-dna-sequence-found-in-p.html
Noh, Y.K., Du, P., Kim, I.G., Ko, J., Kim, S.W., Park, K. (2016). Polymer mesh scaffold combined with cell-derived ECM for osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells. Biomater Res. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27057347/
Noor-A-Rahim, M., John, J., Firyaguna, F., Sherazi, H.H.R., Kushch, S., Vijayan, A., O’Connell, E., Pesch, D., O’Flynn, B., O’Brien, W., Hayes, M., Armstrong. E. (2022). Wireless Communications for Smart Manufacturing and Industrial IoT: Existing Technologies, 5G and Beyond. Sensors (Basel). 23(1):73 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36616671/
Nyström, S., & Hammarström, P. (2022). Amyloidogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 144(20), 8945–8950. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.2c03925
Perez, J.-C., Moret-Chalmin, C. and Montagnier, L. (2023) Emergence of a new Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease: 26 cases of the human version of Mad-Cow Disease, a few days after a COVID-19 injection. International Journal of Vaccine Theory, Practice, and Research, 3, 727–70. https://doi.org/10.56098/ijvtpr.v3i1.66
Reuters. (2021, February 9). Fact check: The COVID-19 vaccine is not an operating system designed to program humans. Reuters. https://www.reuters.com/article/world/fact-check-the-covid-19-vaccine-is-not-an-operating-system-designed-to-program-idUSKBN2A912Y/
Russell, C.L. (2018). 5G wireless telecommunications expansion: Public health and environmental implications. Environ Res, 165:484-495. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29655646/
Santiago, D. (2022). Playing Russian Roulette with every COVID-19 injection: The deadly global game. International Journal of Vaccine Theory, Practice, and Research, 2(2), 619–650. https://doi.org/10.56098/ijvtpr.v2i2.36
Santiago, D. and Oller, J.W. (2023) Abnormal clots and all-cause mortality during the pandemic experiment: five doses of COVID-19 vaccine are evidently lethal to nearly all Medicare participants. International Journal of Vaccine Theory, Practice, and Research, 3, 847–90. https://doi.org/10.56098/ijvtpr.v3i1.73
Segalla, G. (2023a). Adjuvant activity and toxicological risks of lipid nanoparticles contained in the COVID 19 “mRNA vaccines.” International Journal of Vaccine Theory, Practice, and Research, 3(1), 1085–1102. https://doi.org/10.56098/z1ydjm29
Segalla, G. (2023b). Apparent cytotoxicity and intrinsic cytotoxicity of lipid nanomaterials contained in a COVID-19 mRNA vaccine. International Journal of Vaccine Theory, Practice, and Research, 3(1), 957–972. https://doi.org/10.56098/ijvtpr.v3i1.84
Segalla, G. (2023c). Chemical-physical criticality and toxicological potential of lipid nanomaterials contained in a COVID-19 mRNA vaccine. International Journal of Vaccine Theory, Practice, and Research, 3(1), 787–817. https://doi.org/10.56098/ijvtpr.v3i1.68
Seneff, S., Nigh, G., Kyriakopoulos, A.M., McCullough, P.A. (2022). Innate immune suppression by SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccinations: The role of G-quadruplexes, exosomes, and MicroRNAs. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 164. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S027869152200206X?via%3Dihub
Shah KV. SV40 and human cancer: a review of recent data. Int J Cancer. 2007 Jan 15;120(2):215-23. doi: 10.1002/ijc.22425. PMID: 17131333.
Shaw, C. A. (2017). Neural Dynamics of Neurological Disease. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118634523.refs
Shiu, B.C., Liu, Y.L., Yuan, Q.Y., Lou, C.W., Lin, J.H. (2022). Preparation and Characterization of PEDOT:PSS/TiO2Micro/Nanofiber-Based Gas Sensors. Polymers (Basel). 14(9):1780. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35566945/
Spectroscopy and Campra, P. (2021) Detection of graphene in COVID-19 vaccines. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/355979001_DETECTION_OF_GRAPHENE_IN_COVID19_VACCINES
Suberi, A., Grun, M. K., Mao, T., Israelow, B., Reschke, M., Grundler, J., Akhtar, L., Lee, T., Shin, K., Piotrowski-Daspit, A.S., Homber, R.J., Iwasak, A., Suh, H.W., and Saltzman, W.M. (2023). Polymer nanoparticles deliver mRNA to the lung for mucosal vaccination. Science Translational Medicine, 15(709), DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abq0603
Truong, N.P., Quinn, J.F., Whittaker, M.R., and Davis, T.P. (2016). Polymeric filomicelles and nanoworms: two decades of synthesis and application. Polymer Chemistry, 26. https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2016/py/c6py00639f
Vojdani, A., & Kharrazian, D. (2020). Potential antigenic cross-reactivity between SARS-CoV-2 and human tissue with a possible link to an increase in autoimmune diseases. Clinical Immunology (Orlando, Fla.), 217, 108480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2020.108480
Vojdani, A., Vojdani, E., & Kharrazian, D. (2021). Reaction of human monoclonal antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 proteins with tissue antigens: Implications for autoimmune diseases. Frontiers in Immunology, 11, 617089. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.617089
WHO, World Health Organization. 2021. WHO Laboratory Manual for the Examination and Processing of Human Semen. Sixth Edition. https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/343208/9789240030787-eng.pdf?sequence=1
Woodruff, K. and Maerkl, S.J. (2016) A high-throughput microfluidic platform for mammalian cell transfection and culturing. Scientific Reports, Nature Publishing Group. 6, 23937. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep23937
Xie, Y., Kawazoe, N., Yang, Y., and Chen, G. (2021). Preparation of mesh-like collagen scaffolds for tissue engineering. Materials Advances, 3, 1556-1564. https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2022/MA/D1MA01166A
Zhang, S., Chen, Y., Liu, H., Wang, Z., Ling, H., Wang, C. et al. (2020) Hydrogels: room-temperature-formed PEDOT:PSS hydrogels enable injectable, soft, and healable organic bioelectronics. Advanced Materials, 32, 2070005. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202070005
Zhou, H., Mayorga-Martinez, C.C., Pané, S., Zhang, L., and Pumera, M. (2021). Magnetically Driven Micro and nanorobots. Chemical Reviews 121(8):4999-5041. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c01234
Citiți și:
Dr. Geanina Hagimă: Omul de știință român Mihail Roco, de la Inițiativa Națională de Nanotehnologie din SUA, a răspuns solicitării privind nanoparticulele din vaccinuri, nu însă și cercetătorii noștri
Resetarea medicinei sau resetarea omenirii prin nanotehnologie (I)
yogaesoteric
24 septembrie 2024
